Year 3 White Rose Overview
With thanks to Third Space Learning for this overview:
Topics covered in Year 3 White Rose Maths scheme of learning
Year 3 autumn term
- Place value
- Addition and subtraction
- Multiplication and division (A)
Year 3 spring term
- Multiplication and division (B)
- Length and perimeter
- Fractions (A)
- Mass and capacity
Year 3 summer term
- Fractions (B)
- Money
- Time
- Shape
- Statistics
White Rose Maths Year 3 autumn term
In the autumn term, Year 3 focuses on place value, addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.
Place value Year 3
Place value is an essential part of pupils’ learning, hence why it is usually the first block pupils cover each year. In Year 3, several new concepts are introduced as well as recapping important concepts taught in Key Stage 1. In KS1, pupils look at numbers to 100. In Year 3, pupils look at numbers up to 1,000. Pupils also expand their knowledge of counting in multiples by counting in multiples of 50.
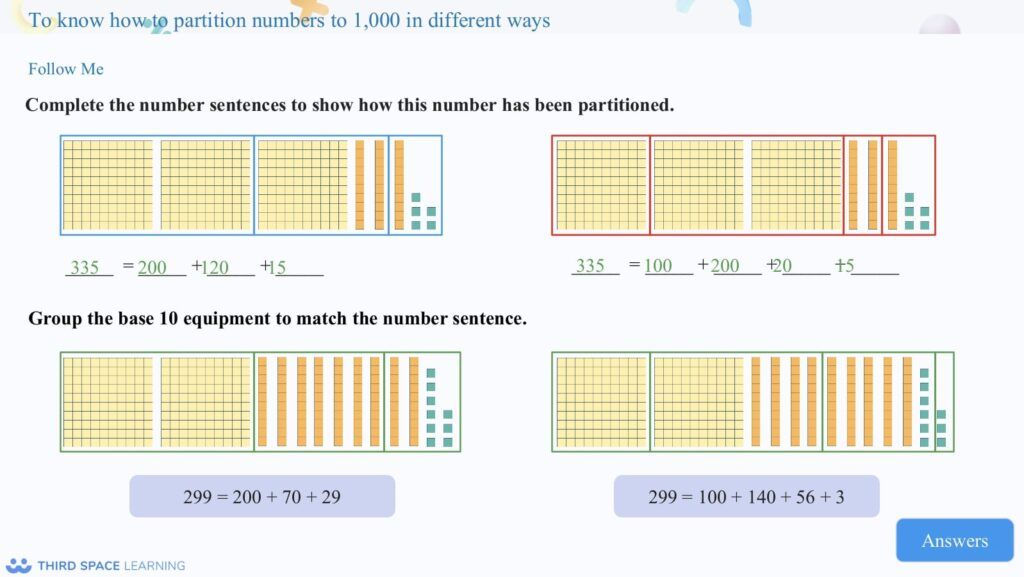

This image shows how place value questions can be put into a real life context and to
recap prior knowledge of measurement.
Example year 3 place value questions:
1. Write 357 in words
Answer: Three hundred and fifty-seven
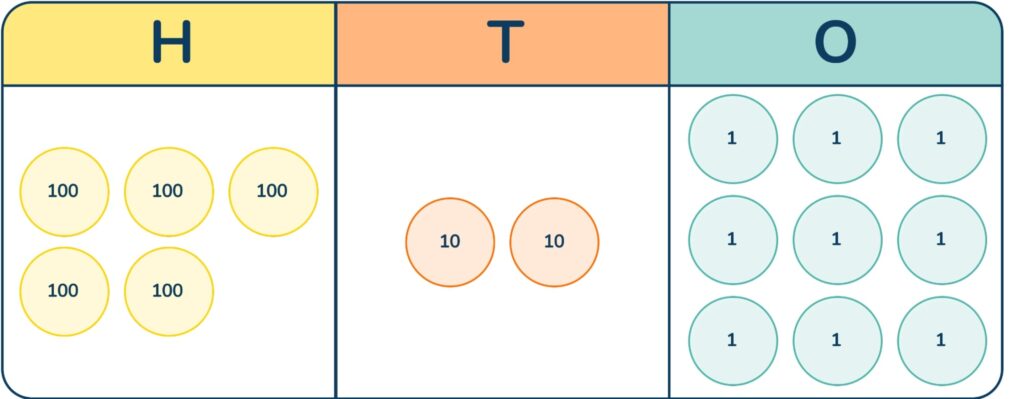
2. Represent 529 using place value counters
Answer:
3. Complete the next two numbers in this sequence: 300, 250, 200, ……, ……
Answer: 150, 100
White Rose Maths year 3 place value resources
- Year 3 place value ready-to-go lesson slides
- Maths Code Crackers Year 3 Place Value
- Number and Place Value Diagnostic Assessments Year 3
- Year 3 Worked Examples Place Value
- Rapid Reasoning Year 3 Weeks 1 to 6
- All Kinds of Word Problems on Number and Place Value Year 3
Addition and subtraction Year 3
In the White Rose Maths scheme of learning version 3, Year 3 is introduced to the formal written method of addition and subtraction. This builds on knowledge of adding and subtracting (including regrouping and exchanging) with concrete resources. This is in addition to other methods of addition and subtraction.
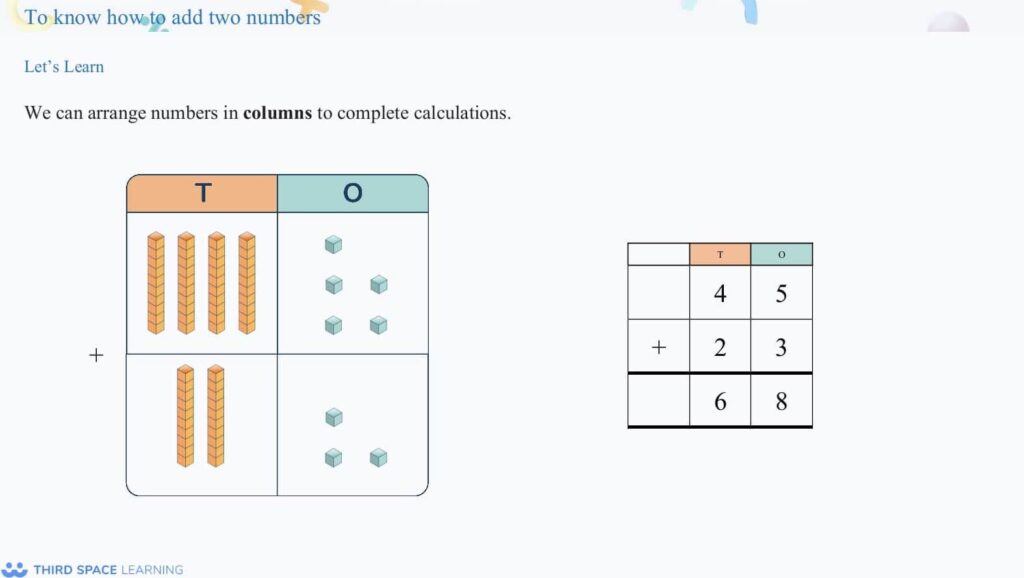
Example of moving from concrete, or pictorial if teachers use the slides
with no physical resources, to abstract in addition.
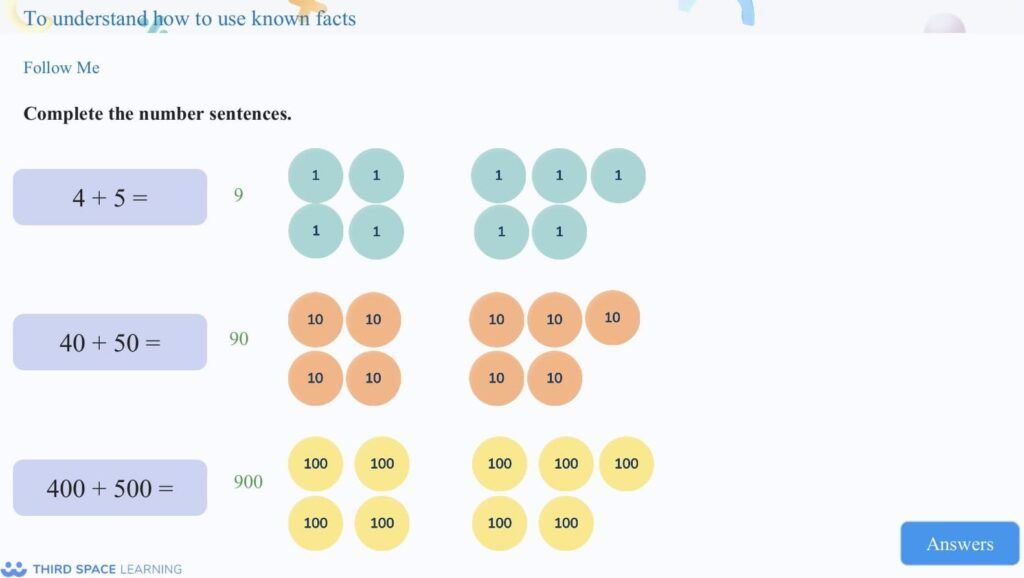
This slide focuses on using known facts to add.
This is an alternative method that pupils can use when completing calculations.
Example year 3 addition and subtraction questions:
1. Complete the calculation: 527 – 300 =
Answer: 227
2. Complete the calculation: 349 + 218 =
Answer: 567
3. Lola has £436. She spends £172. How much money does she have left?
Answer: £264
White Rose Maths Year 3 addition and subtraction resources
- Ready-to-go Lessons Year 3 Addition and Subtraction
- Ready-to-go lessons Year 3 Addition and Subtraction (Autumn Block 2) Slides and Worksheets
- Maths Code Crackers Year 3 Addition and Subtraction
- Addition and Subtraction Diagnostic Assessments Year 3
- Year 3 Worked Examples Addition and Subtraction
- All Kinds of Word Problems on Addition and Subtraction Year 3
Multiplication and division Year 3
Multiplication and division has been divided into two blocks, Multiplication and Division A in Autumn and Multiplication and Division B in Spring.
Multiplication and division A
Multiplication and division has been divided into two blocks, one in Autumn and one in Spring. The autumn term block focuses on basic understanding such as equal groups, arrays and sharing and grouping as well as recapping times table facts from Year 2 (2s, 5s and 10s) and introduces other times tables facts (3s, 4s and 8s).
The 3, 4 and 8 times tables are introduced as both multiplication and division facts to reinforce the link between multiplication and division. Year 3 also explores the relationship between the 2, 4 and 8 times tables.
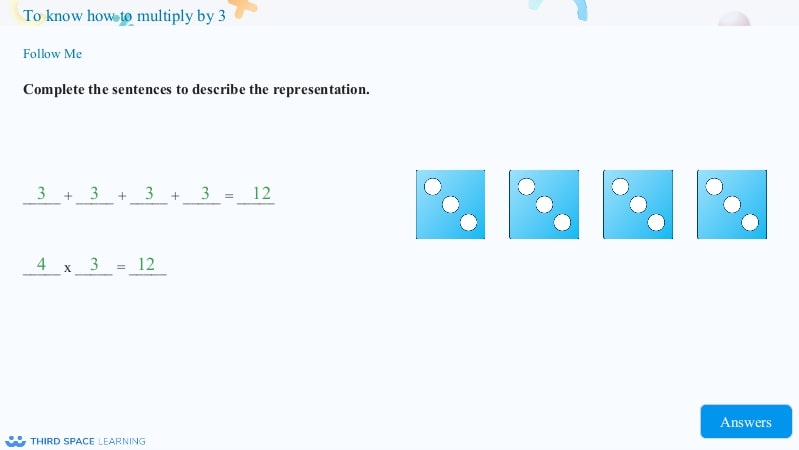
This explores the relationship between repeated addition and multiplication.
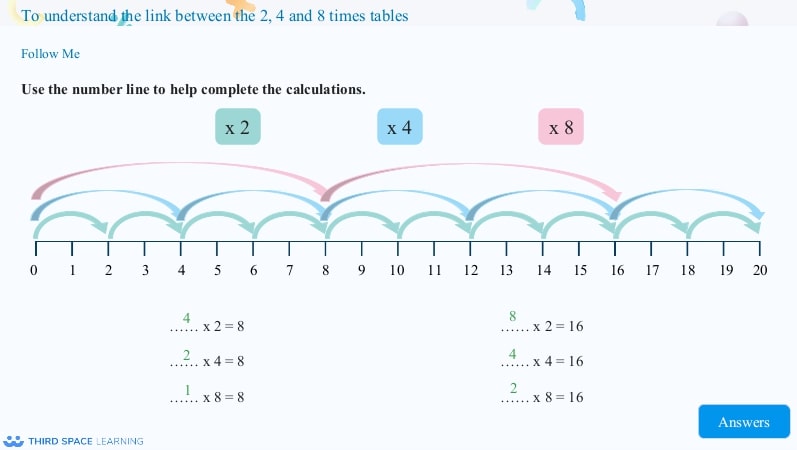
Lesson slide illustrating the relationships between x2, x4, x8
Example year 3 multiplication and division A questions:
1. Adam has 4 bags of cookies. Each bag holds 3 cookies. How many cookies does Adam have in total?
Answer: 4 x 3 = 12
2. Complete the calculation: 36 ÷ 4 =
Answer: 9
3. Complete the grid:
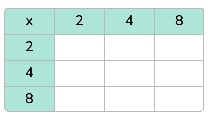
Answer: Row 1: 4, 8, 16, Row 2: 8, 16, 32, Row 3: 16, 32, 64
White Rose Maths Year 3 multiplication and division resources
- Ready-to-go Lessons Year 3 Multiplication and Division A
- Ready-to-go Lessons Year 3 Multiplication and Division B
- Ready-to-go lessons Year 3 Multiplication and Division (Spring Block 1) Slides and Worksheets
- Maths Code Crackers Year 3 Multiplication and Division
- Multiplication and Division Diagnostic Assessments Year 3
- Year 3 Worked Examples Multiplication and Division
White Rose Maths Year 3 spring term
In the spring term, Year 3 continues with multiplication and division and covers length, perimeter and fractions.
Multiplication and division B Year 3
Once pupils are more confident with times tables facts, they then move on to multiplying and dividing with a 2-digit and a 1-digit number. In Year 3, pupils will not use formal methods (such as short multiplication or short division), instead they focus on using concrete resources such as counters.
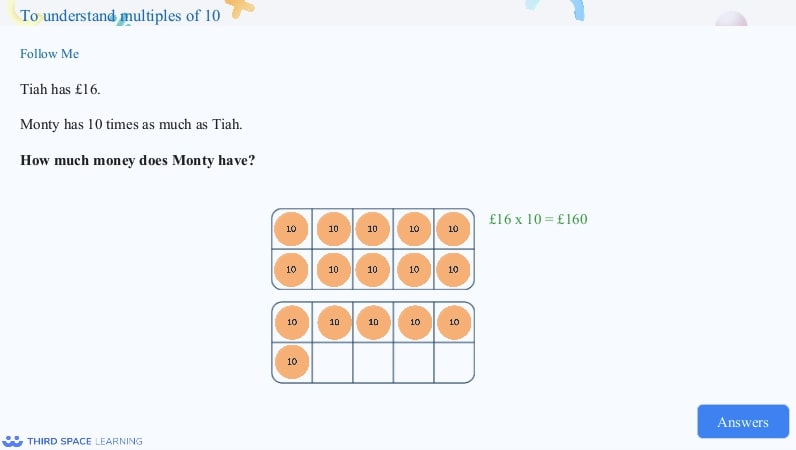
Example of multiplying by 10 using concrete resources and in context.
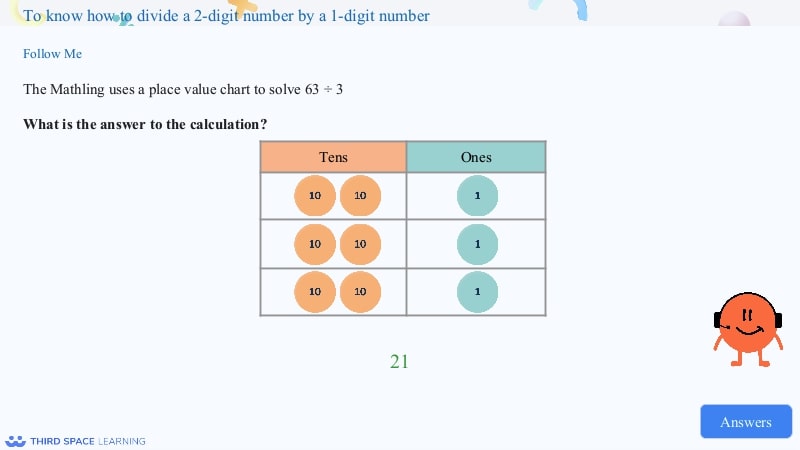
Example of dividing a 2-digit number by a 1-digit number using concrete resources.
Example year 3 multiplication and division B questions:
1. Complete the calculation: 17 x 10 =
Answer: 170
2. Complete the calculation: 23 x 3 =
Answer: 69
3. Complete the calculation: 64 ÷ 4 =
Answer: 16
Length and perimeter Year 3
Pupils will be familiar with measuring lengths in metres and centimetres from Year 2. In Year 3, they expand this understanding by measuring in millimetres as well as measuring in mixed units (centimetres and metres). Pupils will also explore equivalent lengths and learn about perimeter for the first time. The study of perimeter starts with pupils understanding that perimeter is the distance around a closed 2-D shape.
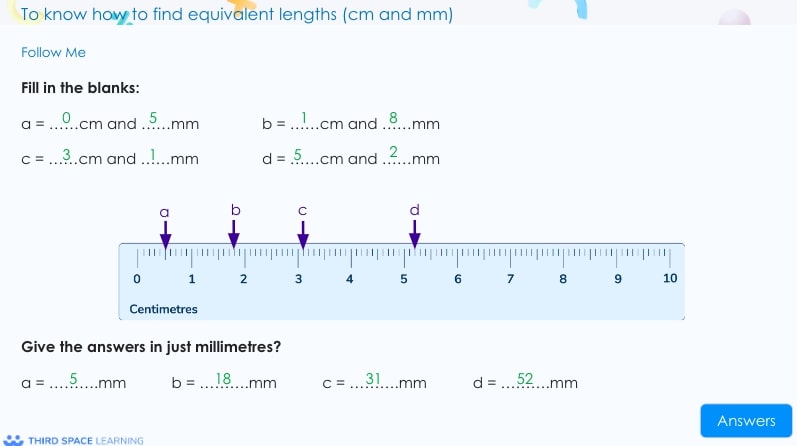
This shows equivalent measures between centimetres and millimetres.
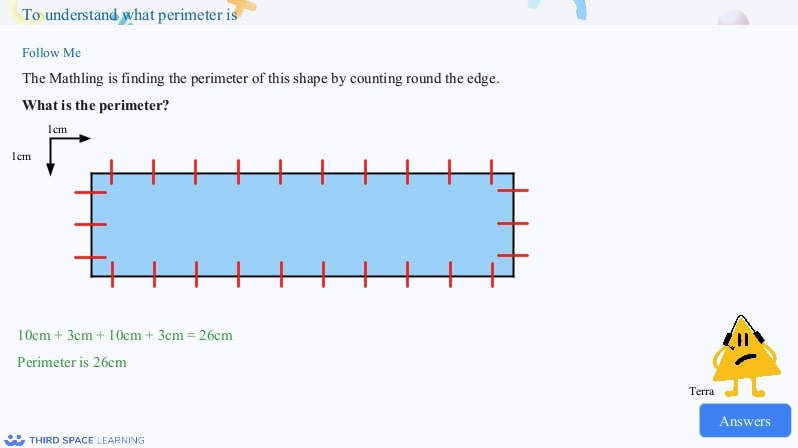
Introduction to perimeter by counting squares.
Example year 3 length and perimeter questions:
1. Compare the lengths 5cm & 5mm
Answer: 5cm > 5mm
2. Convert 3m and 46cm into centimetres.
Answer: 346cm
3. A square has sides measuring 5cm. What is the perimeter of the square?
Answer: 20cm
White Rose Maths Year 3 length and perimeter resources
- Ready-to-go Lessons Year 3 Length and Perimeter
- Ready-to-go lessons Year 3 Length and Perimeter (Spring Block 4) Slides and Worksheets
- Year 3 Worked Examples Length and Perimeter
- Maths Code Crackers Year 3 Length and Perimeter
Fractions Year 3
Like multiplication and division, fractions is split across two terms, Fractions A is in the spring term and Fractions B in the summer term.
Fractions A Year 3
Fractions A block focuses on understanding fractions including unit and non-unit fractions and representing fractions on number lines. There is also a focus on identifying equivalent fractions.
The entire topic block on fractions in Year 3 relies on concrete and pictorial representations to solidify pupils’ understanding of the mathematical concept of fractions.
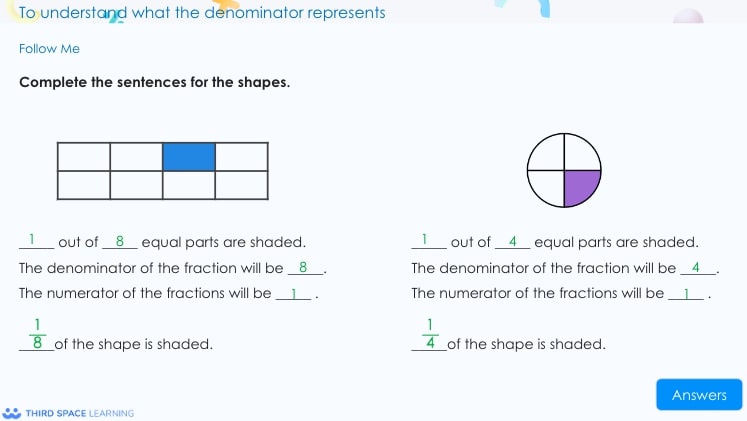
Understanding the denominator in unit fractions.
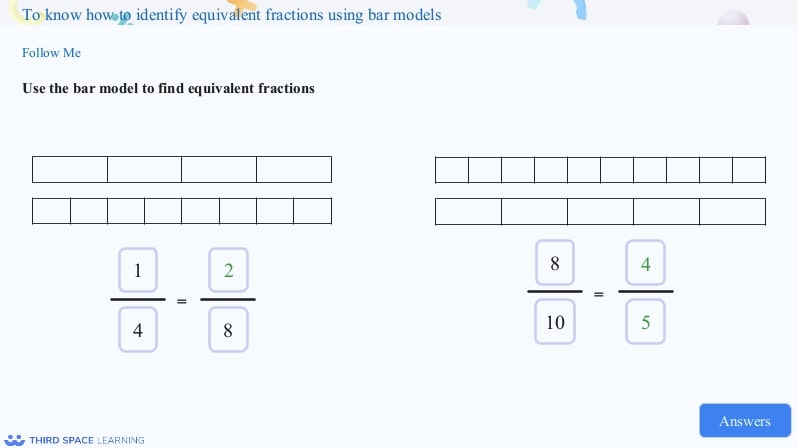
Using bar models to find equivalent fractions.
Example Year 3 fractions A questions:
1. Use bar models to help compare these fractions: 1771 & 1221
Answer: 1771 < 1221
2. What fraction is represented by the bar model?
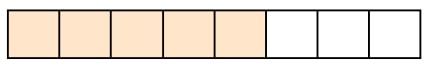
Answer:5885
3. Use the bar model to find the equivalent fractions. 610106 = ?55?
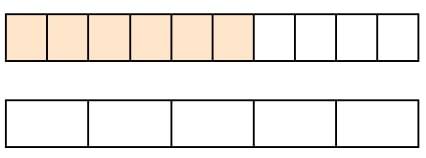
Answer: 610106 = 3553
White Rose Maths Year 3 fractions resources
- Ready-to-go Lessons Year 3 Fractions A
- Ready-to-go lessons Year 3 Fractions (Spring Block 5) Slides and Worksheets
- Ready-to-go lessons Year 3 Fractions (Summer Block 1) Slides and Worksheets
- Tarsia Puzzle Subtract Fractions (Year 3)
- Tarsia Puzzle Fractions of Amounts (Year 3)
- Tarsia Puzzle Equivalent Fractions (Year 3)
- Tarsia Puzzle Add Fractions (Year 3)
- Fractions Diagnostic Assessments Year 3
- Year 3 Worked Examples Fractions
- Maths Code Crackers Year 3 Fractions
Mass and capacity Year 3
In Year 3, pupils recap reading scales in grams and millilitres. This is extended with pupils focusing on measuring mass in grams and kilograms as well as measuring capacity or volume in millilitres and litres.
Pupils will measure mass using weighing scales and learn to measure capacity and volume using measuring jugs. Pupils will also explore equivalent masses and equivalent capacities or volumes. They will also compare masses and compare capacities or volumes.
Example Year 3 mass and capacity questions:
1. What is the mass of the car? _____kg and _____g
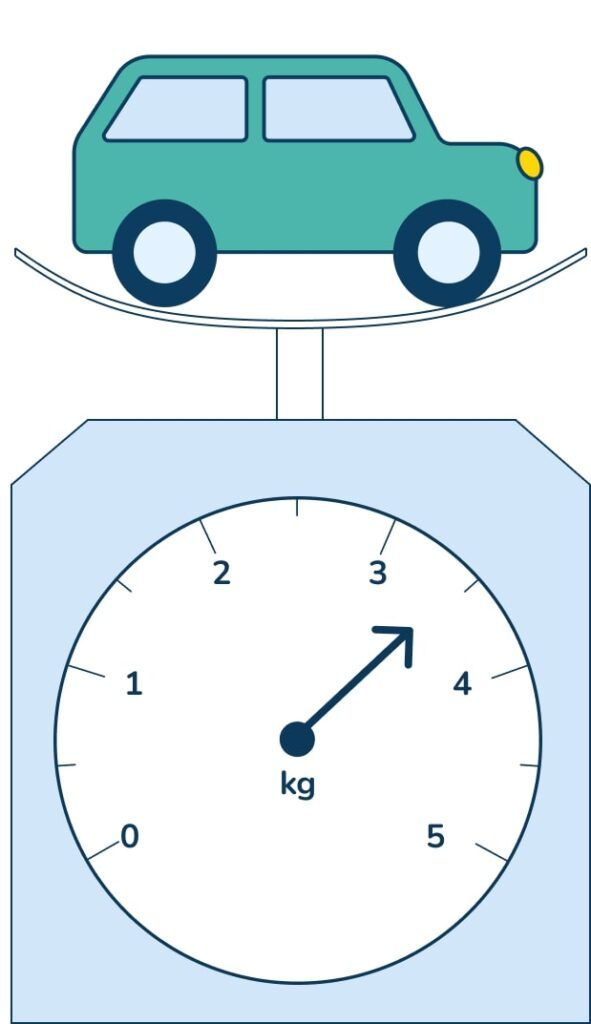
Answer: 3kg and 500g
2. Joanne has 500g of sweets. Marcy has 650g of sweets. What is the total mass of their sweets?
Answer: 1kg and 150g
3. I have 400ml of water. How much more water would I need to make 1 litre of water?
Answer: 660ml
White Rose Maths Year 3 mass and capacity resources
- Ready-to-go lessons Year 3 Mass and Capacity (Summer Block 4) Slides and Worksheets
- Year 3 Worked Examples Mass and Capacity
- Maths Code Crackers Year 3 Mass and Capacity
White Rose Maths Year 3 summer term
During the summer term, the White Rose Maths Year 3 SOL continues with fractions and covers money, time, shape and statistics.
Fractions B Year 3
The summer term fractions block focuses on calculating with fractions, this involves adding and subtracting fractions with the same denominator. Pupils build upon their learning from Year 2 (where they found 1221, 1441, 1331 or 3443 of a set of objects) by finding fractions of objects and amounts. They will focus on finding unit and non-unit fractions of objects and amounts.
Example Year 3 fractions B questions:
1. Add these fractions: 411114 + 311113 =
Answer: 711117
2. Use the bar model to complete the calculation. 2772 + ? = 1
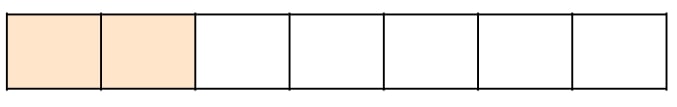
Answer:2772 + 5775 = 1
3. Complete the calculation: 1551 of 15 =
Answer: 3
Money Year 3
In Year 3 , pupils focus on expressing money as pounds and pence, not involving decimals.
Pupils look at converting coins, notes or given amounts in pence into amounts written as pounds and pence. Pupils also calculate using money with pounds and pence. This includes finding change, a valuable skill for any child to understand.
Example Year 3 money questions:
1. Complete the conversion: 163p = £___ and ___p
Answer: £1 and 63p
2. Complete the calculation: £2 and 30p + £4 and 85p =
Answer: £7 and 15p
3. Charlie buys a new notebook. She pays using a £5 note. She is given £2 and 30p change. How much does the notebook cost?
Answer: £2 and 70p
White Rose Maths Year 3 money resources
- Ready-to-go lessons Year 3 Money (Spring Block 2) Slides and Worksheets
- Year 3 Worked Examples Money
- Maths Code Crackers Year 3 Money
Time Year 3
Pupils begin learning time in Year 2, in Year 3 they expand their knowledge by looking at clocks that have numbers in digits and Roman numerals. Pupils tell the time to the nearest 5 minutes and the nearest minute.
Pupils are also introduced to reading time on digital clocks and understand am and pm times. Pupils look at facts around years/ months/ days (calendars) as well as facts about days and hours (e.g. how many days in a non-leap year, how many hours in a week). They also calculate durations and convert between minutes and seconds. Finally, they will solve problems involving time such as time word problems.
Example Year 3 time questions:
1. Which time is the earliest in the day? 7:30pm or 7:30am
Answer: 7:30am
2. How many days are in a school week?
Answer: 5
3. The Year 3 maths lesson starts at 10:15. It lasts for 50 minutes. What time does it end?
Answer: 11.05
White Rose Maths Year 3 time resources
- Ready-to-go lessons Year 3 Time (Summer Block 2) Slides and Worksheets
- Year 3 Worked Examples Time
- Maths Code Crackers Year 3 Time
Shape Year 3
In Year 3, pupils are introduced to angles. They focus on right angles (not measuring in degrees). They identify right angles and compare other angles to right angles (e.g. greater than or less than a right angle). Pupils are also introduced to the terms acute and obtuse.
Pupils look at types of lines (horizontal and vertical, parallel and perpendicular) and recognise and draw 2-D shapes and make 3D shapes.
Example Year 3 shape questions:
1. Draw two different angles that are less than a right angle
Answer: Accept any two different acute angles.
2. Tick the lines that are parallel.
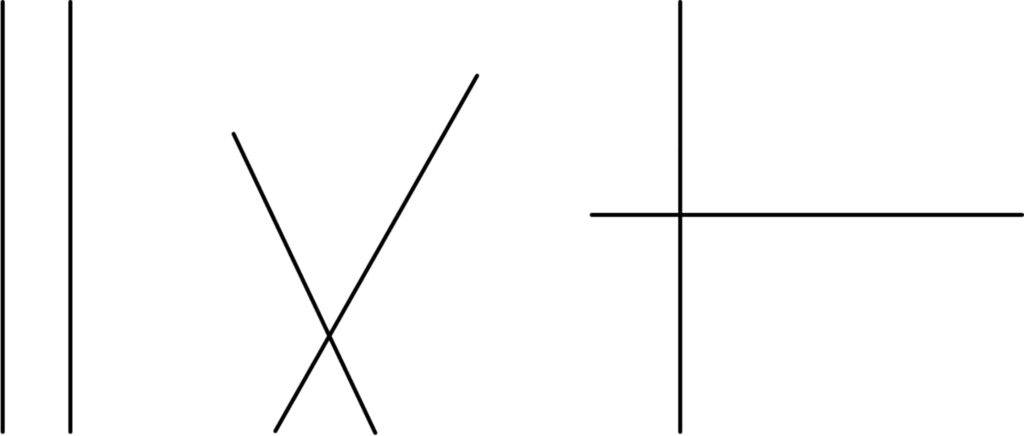
Answer:
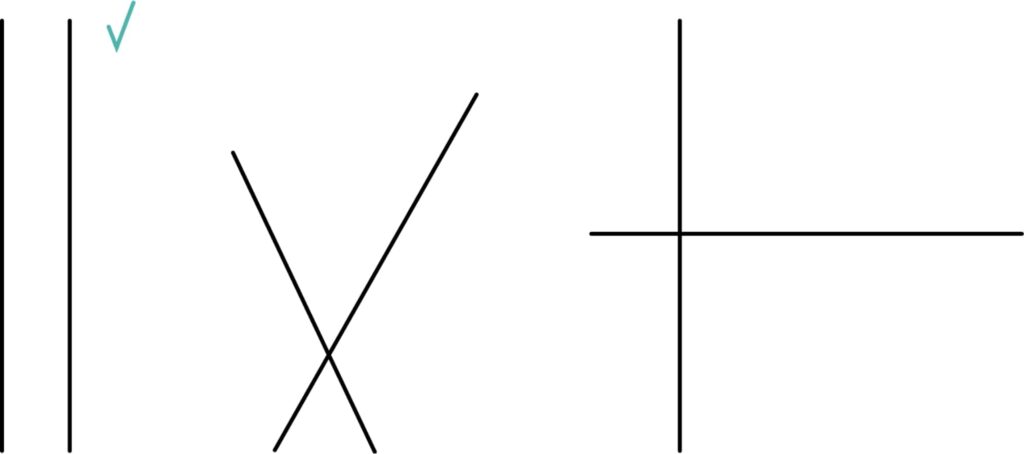
3. Draw two different quadrilaterals.
Answer: Accept any two different quadrilaterals.
White Rose Maths Year 3 shape resources
- Ready-to-go lessons Year 3 Properties of Shape (Summer Block 3) Slides and Worksheets
- Year 3 Worked Examples Properties of Shape
- Maths Code Crackers Year 3 Properties of Shape
Statistics Year 3
In Year 3, pupils move beyond block diagrams (taught in Year 2) to bar charts. They also recap interpreting and drawing pictograms. In version 3 of the White Rose Maths Year 3 scheme of learning, pupils are introduced to two-way tables for the first time.
Example Year 3 statistics questions:
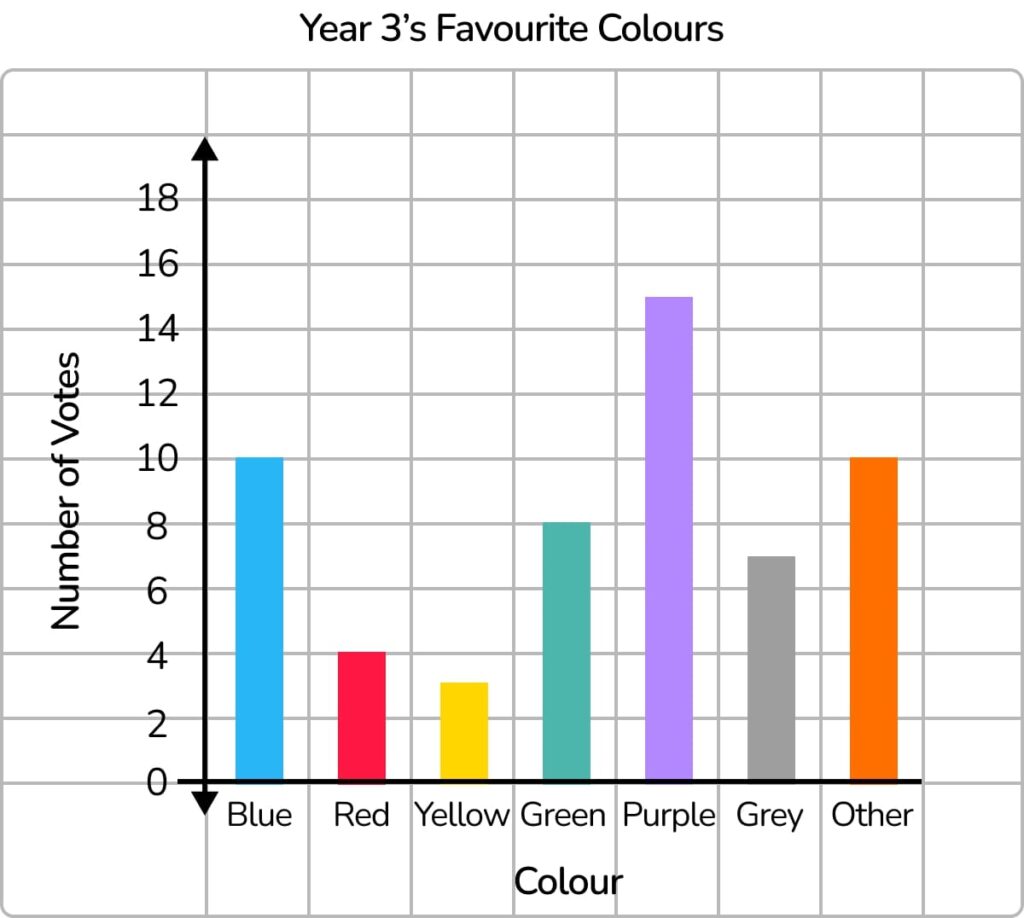
1. How many children voted for green?
Answer: 8
2. Which colour was the most popular?
Answer: purple
3. How many children are in Year 3?
Answer: 57
